
One curious feature of the expression in equation (5) is that the lattice energy has the largest magnitude when r = 0! The model does not implicitly include any repulsion between unlike charges. Solids adopt structures with higher coordination numbers to maximize the ionic bonding Note that, for a given stoichiometry, the Madelung constant and, hence, the lattice energy, increase with the coordination number: The final column shows the Madelung constant divided by the number of ions in the chemical formula. The Madelung constant for common MX and MX 2 structures. The table below lists the Madelung constant for a number of common structural types. Every compound with the rocksalt structure has the same Madelung constant. The Madelung constant depends only on the crystal structure not on the size or charge of the ions.
#Chemical equation for lattice energy of nacl series
Where the Madelung Constant, A, is the numerical value of the infinite series summation. As this counts every interaction twice, it is then necessary to divide by two giving the total energy as: This summation is repeated for every ion in the crystal (i.e. The net attractive energy between the Na + ion and all other ions in the crystal is given by the infinite (and slowly converging series): In the next shell, the Na + ion experiences an attractive potential energy with the eight Cl- ions at the corner of the unit cell, at a distance of (3) 1/2r: This gives rise to a repulsive potential energy term: The next nearest neighbours for the Na + ion are the twelve Na + ions on each edge of the unit cell, at a distance of (2) 1/2r. In the sodium chloride structure, the Na + ion at the centre is surrounded by six Cl - at a distance r. Where e is the charge on an electron, ε 0 is the permittivity of a vacuum and r is the distance between the centres of the ions. If the charges on the cation and anion are q 1 and q 2, the attractive interaction between a pair is: We first use this model to calculate the lattice energy and then show how the model is improved by including the compressibility of the ions. The simplest model imagines that the ions are hard spheres with fixed radii. The distance between the ions is determined by the balance of the attractive force between cation and anion and the repulsive forces between both the core electrons of the ions and their nuclei. The unit cell is the simplest structure that generates the whole lattice when repeated infinitely in all directions. The structure can be rotated with the mouse. The unit cell for the rocksalt structure of NaCl is shown opposite.
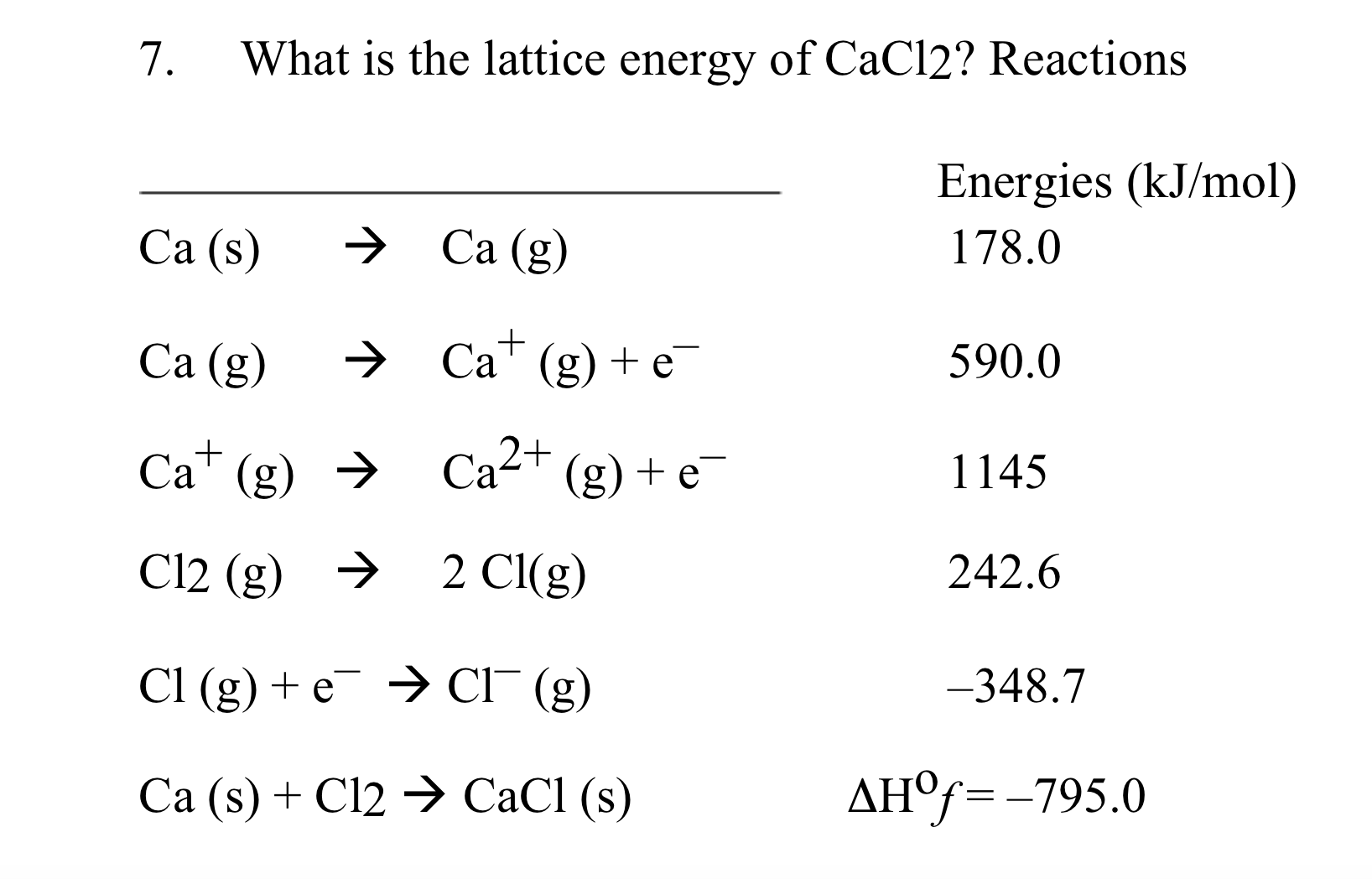
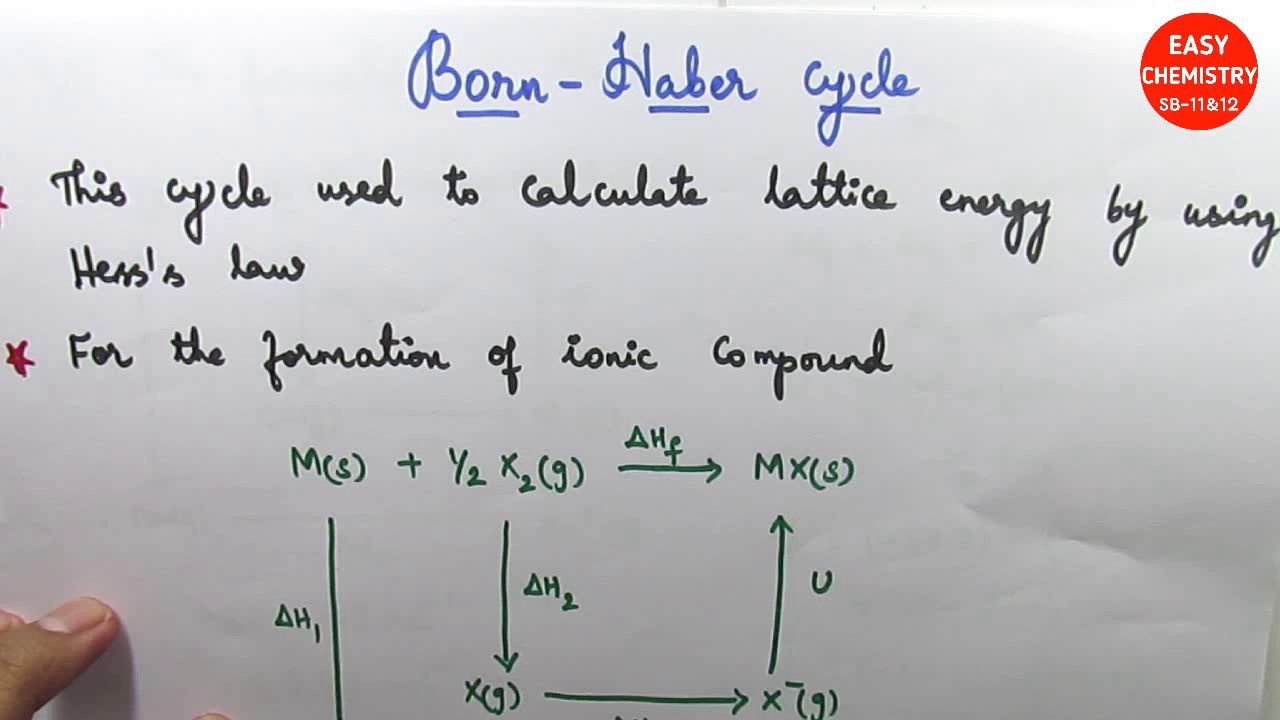
The energy that is required to completely separate the ions is called the lattice energy.
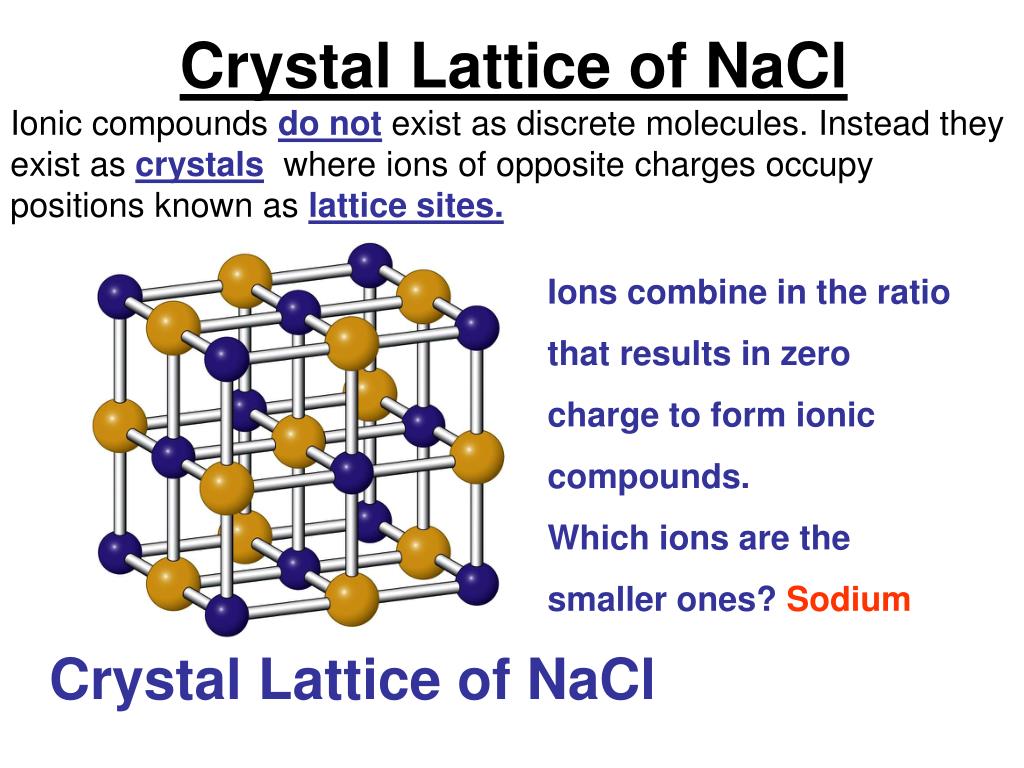
They are held together in three-dimensional arrangements by the attractive forces between every pair of oppositely charged ions – not just by the interaction between neighbouring ions. Ionic compounds are usually solids at room temperature, although ionic liquids also exist. The compounds formed between elements of very different electronegativities are usually ionic in character. The pre-work revises and extends the material presented in the lecture course. In this experiment, the structures of many elements and compounds are rationalized using simple packing models.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
