

Total Internal Reflection takes place when light travels from a denser medium to a lighter medium. If the angle of incidence is increased further, so that it is greater than the critical angle, the light will be totally internally reflected. Total internal reflection takes place in electromagnetic waves, light waves, microwaves, sound waves as well as water waves. The diagram below shows light hitting the glass-air boundary at an angle that is equal to the critical angle. Total internal reflection is the complete reflection of light at the boundary between two media, caused by the angle of incidence being greater than the. You will be reminded of this fact in the exam. This is called total internal reflection. The critical angle is defined as the angle of incidence in a.

A light ray might move from a denser medium toward a rarer medium. The critical angle varies for different materials, but it is useful to know that it is around 42 degrees for glass. When the angle of refraction is equal to \(90\circ\), the angle of incidence is called the critical angle, \. Total internal reflection, coupled with a large index of refraction, explains why diamonds sparkle more than other materials. The two conditions for the total internal reflection to take place are as follows: Throughout the denser medium, the angle of incidence mustve been larger than the critical angle for this kind of combination of media. This angle of incidence is called the critical angle. At a certain angle of incidence, the light will refract 90 degrees and travel along the boundary between the two media. The diagram below shows the light refracting from glass into air.Īs the angle of incidence is increased, the angle of refraction also increases.
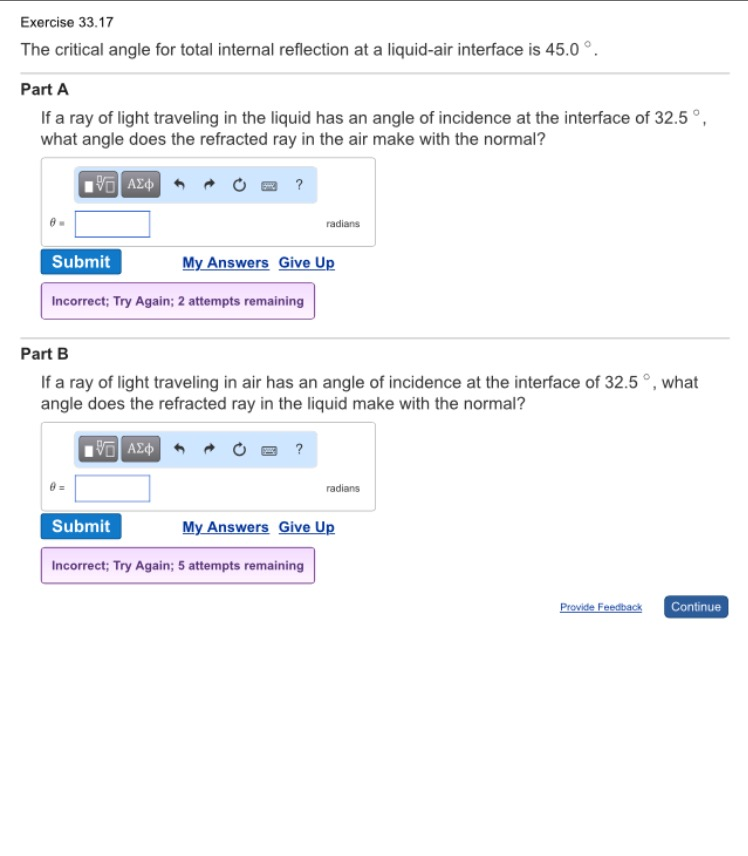
The angle of refraction is greater than the angle of incidence. When light travels from a denser medium, eg glass, to a less dense medium, eg air, the speed of the light increases and the light refracts away from the normal. As the incident ray approaches the critical angle (approximately 42o) the refracted ray travels at right-angles to the normal. The measure of the critical angle depends on the properties of. When light travels into a different medium, the speed of the light changes and the light is refracted (see The features of waves ). The critical angle defines a limit for an angle of incidence to cause total internal reflection. The conditions for total internal reflection


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
